Will Skipping Meals Spike Your Metabolism
Intermittent Fasting: Optimal Health Benefits for Metabolism
Intermittent fasting has become a popular topic among health enthusiasts seeking to optimize weight loss and promote overall health. This mealtime schedule involves cyclically alternating between consuming and abstaining from food, which can significantly modify your metabolic rate and body composition.
Learn about the science of intermittent fasting and its impact on hunger levels, fat-burning potential, and brain function compared to other dietary approaches. Discover the difference between skipping meals and low-calorie diets, highlighting their effects on hunger. Additionally, we'll delve into combining keto with intermittent fasting for enhanced fat-burning potential and improved brain function.
The Difference Between Skipping Meals and Low-Calorie Diets
Understanding the difference between intermittent fasting and a low-calorie diet is essential to understanding their impact on metabolic processes, which can significantly impact your weight loss journey.
Intermittent Fasting vs. Low-Calorie Diets
Intermittent fasting (IF) involves alternating periods of eating with periods of fasting.
This approach does not necessarily focus on reducing calorie intake but changes the timing of food consumption. IF has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, increase fat burning, and promote overall health benefits.
In contrast, low-calorie diets consistently consume fewer calories than required to maintain body weight. This method often causes a slow metabolism as the body adapts to lower energy intake levels over time.
Effects on Hunger Levels
Intermittent fasting: Many people find that their hunger levels decrease during fasting periods due to hormonal adaptations such as reduced ghrelin production (the "hunger hormone"). Additionally, IF allows individuals to consume larger meals within their eating window without exceeding daily caloric needs.
Low-calorie diets: On a low-calorie diet plan, constant calorie restriction may increase feelings of hunger and cravings throughout the day. Over time, this could result in a slower metabolism as the body conserves energy.
It is essential to differentiate between these two approaches when discussing metabolic rates because they have different effects on hunger levels and overall weight loss success. Intermittent fasting allows for sustainable caloric intake during eating windows, leading to increased satiety.
This explains why intermittent fasting is significantly more successful than unsustainable low-calorie diets. Furthermore, intermittent fasting may help maintain or even increase your metabolic rate due to its positive impact on insulin sensitivity, fat-burning processes, and growth hormone levels.

Keto Diet Combined with Intermittent Fasting
Combining a low-carb ketogenic diet with intermittent fasting can help you adapt to burning stored body fat for energy instead of relying on glucose from carbohydrates.
This powerful combination reduces hunger levels and boosts weight loss success compared to traditional low-calorie diets.
Benefits of Keto-Adaptation for Fat Burning
The process of keto-adaptation involves training your body to use ketones derived from fat breakdown as its primary fuel source.
Following a ketogenic diet and practicing intermittent fasting, your body can access stored fats for energy. Some benefits of ketosis include:
Sustained energy levels throughout the day without experiencing sugar cravings and energy crashes.
Better mental clarity and focus due to stable blood sugar levels.
Lower risk of insulin resistance linked to type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
A natural reduction in appetite makes it easier to maintain intermittent fasting and keto, making it a sustainable choice for long-term weight management.
How Ketones Support Brain Function
A study published by The FASEB Journal indicates that ketones may offer numerous cognitive benefits besides supplying an alternative fuel source for the body during low-carb consumption. The study suggests that ketone bodies can cross the blood-brain barrier, provide adequate fuel for brain cells, and support neuroprotective effects on the central nervous system.
Ketones can support brain functions because they:
Enhance mitochondrial function which is crucial for energy production and overall brain health.
Support the reduction of brain inflammation, which has been linked to neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Promote the growth of new neurons and synapses, leading to improved learning and memory functions.
Incorporating a ketogenic diet with intermittent fasting supports weight loss efforts and provides numerous benefits for cognitive function. Adapting the body to burn fat more proficiently with this dietary approach can increase mental acuity, sharper concentration, and reduce hunger, which makes it easier to adhere to this dietary regimen.
Insulin's Role in Metabolism Regulation
Comprehending the association between insulin levels, how often you eat, and your metabolic rate is essential when discussing metabolic health. Insulin is a hormone the pancreas produces that regulates blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy or storage as fat.
By decreasing meal frequency without significantly cutting calories, you can lower insulin production, increasing your metabolic rate, resulting in more effective weight loss.
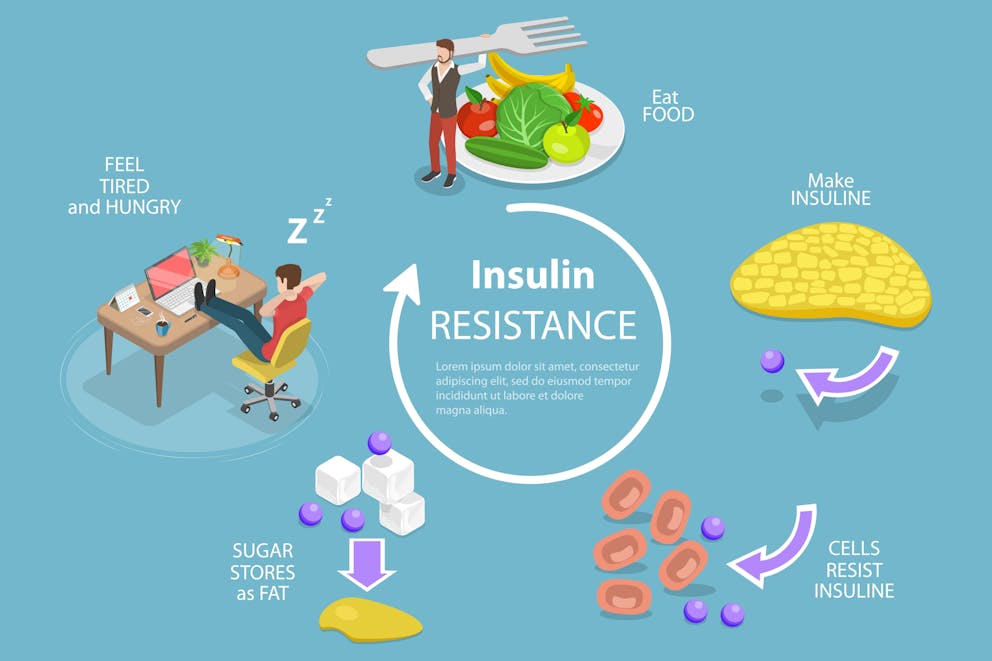
Insulin Resistance Risk Factors
Insulin resistance occurs when cells do not respond effectively to insulin signals, leading to higher blood sugar levels and increased insulin production. This condition has been linked to obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other health issues.
Some risk factors for developing insulin resistance include:
A sedentary lifestyle with little physical activity
Poor diet high in processed foods, carbs, and sugars
Frequent snacking
Genetic predisposition or family history of diabetes
Hormonal imbalances such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Certain medications like corticosteroids or antipsychotics
Strategies for Lowering Insulin Levels
To improve your metabolism through better regulation of insulin levels, consider implementing some of these strategies:
Incorporate intermittent fasting: As mentioned earlier, reducing meal frequency can help lower overall daily insulin production while maintaining adequate caloric intake.
Adopt a low-carb diet: A study published by Nutrition & Metabolism has shown that reducing carbohydrate intake can help lower insulin levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
Increase physical activity: Regular exercise, especially resistance training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT), can help improve insulin sensitivity by increasing muscle glucose uptake.
Maintain healthy body weight: Losing excess body fat through intermittent fasting and increased physical activity is essential for improving insulin sensitivity.
Avoid processed foods: Consuming whole, unprocessed foods rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants will support overall health while helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
Taking control of your metabolism involves understanding the role of hormones like insulin in regulating energy balance. By implementing strategies to lower insulin production, you can achieve better metabolic health and more effective weight loss results.
Factors Affecting Your Metabolism Rate
Understanding the various factors that impact your metabolism beyond age or caloric intake can provide insight into personalizing dietary habits that support optimal metabolic health.
This section will dive into early-life nutrition influences on later metabolism and stress-reduction techniques for cortisol reduction.
Early Life Nutrition Influences Later Metabolism
Your body's metabolic rate is influenced by your current diet and the nutrition you receive during early life. Studies have demonstrated that inadequate maternal nutrition during gestation can reduce metabolic rates in the child’s lifespan.
This is caused by inadequate nutrient supply during fetal development, which may result in long-lasting changes to an individual's energy expenditure and fat storage capacity.
Prenatal care: Ensuring proper prenatal care and adequate nutrient intake during pregnancy is crucial for setting up a healthy foundation for your child's future metabolic health.
Breastfeeding: Breast milk contains essential nutrients required for optimal growth and development of infants. Research suggests breastfeeding may help promote a healthier metabolism later in life than formula feeding.
Stress Management Techniques for Cortisol Reduction
Cortisol, commonly known as the "stress hormone," is essential in regulating our body's response to stress.
However, chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels can negatively impact metabolism by promoting insulin resistance, increasing inflammation, and contributing to weight gain.
Effective stress management techniques can help lower cortisol levels and support a healthier metabolic rate.
Deep breathing practices, walking in nature, gardening, or hiking have been shown to reduce stress levels and decrease cortisol production.
Engaging in regular physical activity not only helps burn calories but also releases endorphins that combat stress hormones like cortisol.
Prioritizing quality sleep is essential for regulating hormone production, including cortisol.
Consuming a proper diet rich in whole foods such as healthy fats, proteins, full-fat dairy, organic vegetables, berries, seeds, and nuts provides your body with the necessary nutrients to manage stress effectively.
The Role of Intermittent Fasting in Metabolism
Fasting promotes fat loss by allowing for metabolic switching between glucose burning while eating and fatty acid oxidation during fasting. This results in lower insulin levels, which promotes the release of fatty acids from fat cells to promote ketosis. In this metabolic state, fats are burned as fuel instead of carbohydrates.
Intermittent fasting has been shown to reduce fasting insulin levels, increase human growth hormone production, and improve insulin sensitivity.
What Are Metabolic Body Types?
The three main metabolic body types are ectomorphs, mesomorphs, and endomorphs. Each type has its unique characteristics regarding weight management and overall health.
Ectomorph: Ectomorphs tend to be naturally thin with a fast metabolism. They have trouble gaining weight but struggle maintaining muscle mass if they don't eat enough protein or regularly engage in strength training exercises.
Mesomorph: Mesomorphs have a medium build with well-defined muscles. They typically gain muscle quickly but can also put on fat if they consume too many calories without exercising enough.
Endomorph: Endomorphs tend to have a larger bone structure with more body fat than the other two types. They may find it harder to lose weight due to their slower metabolism but can still achieve success through proper nutrition and exercise habits.
Conclusion
Intermittent fasting is a popular approach to weight loss and improving metabolic health. It has been demonstrated to be more efficient than low-calorie diets in reducing fasting insulin levels and promoting fat loss while preserving muscle mass.
Combining a low-carb keto diet with intermittent fasting can enhance fat-burning and improve brain function. Fasting also lowers the risk of insulin resistance linked to several metabolic diseases, including diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
To gain personalized insights and optimize your approach, take a quiz that factors in your body type, lifestyle, and health goals.
FAQs
1. Does Intermittent Fasting Speed Up Your Metabolism?
Yes, intermittent fasting can help increase your metabolism by promoting the production of human growth hormone (HGH) and reducing insulin levels.
These hormonal changes lead to an increased metabolic rate, which aids in weight loss and improves overall health.
2. How Does Intermittent Fasting Change Metabolism?
Intermittent fasting changes metabolic energy-making processes by shifting the body's primary fuel source from glucose to stored body fat.
This process is called ketosis, during which ketone bodies are produced as an alternative energy source for cells. The result is enhanced fat-burning and improved metabolic efficiency.
3. Why Is 16 Hours the Magic Number for Fasting?
The 16-hour fast duration has been popularized due to its effectiveness in inducing ketosis, allowing sufficient time for glycogen depletion and initiating fat-burning processes.
Additionally, it provides a manageable eating window that fits well into most people's daily routines.
4. What Happens to Metabolism During Fasting?
During fasting, insulin levels decrease while glucagon and HGH levels increase. This hormonal shift promotes lipolysis (fat breakdown), releasing fatty acids from adipose tissue that are converted into ketones.
These are an alternative energy source, resulting in a more efficient metabolic state called ketosis.
Tags

Popular
08/21/2024
46.3K views
05/22/2024
40.8K views
11/18/2024
241.7K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




