Vitamin D3 and K2 Benefits – How They Work Together

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D

Vitamin D – Benefits and Deficiency Warning Signs
Learn to recognize early signs of vitamin D deficiency
Discover how to maintain healthy vitamin D levels
Explore common factors that can contribute to vitamin D deficiency
Understand why vitamin D3 and K2 should always be taken together
Get practical advice on how to maximize the health benefits of vitamin D
Vitamin D3 and vitamin K2 are essential vitamins that work in synergy to regulate calcium levels, promote bone health, and play a vital role in lowering the risk of heart disease.
Maintaining adequate levels of vitamin D3 and K2 is crucial to maintain skeletal and cardiovascular health.
Discover four vitamin D3 and K2 benefits and learn why you should always take vitamin D3 supplementation in combination with vitamin K2.
What is vitamin D3?
Vitamin D, also known as the sunshine vitamin, is a fat-soluble nutrient that’s produced when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet (UVB) radiation in sunlight.
UVB rays can penetrate the skin and stimulate the biochemical conversion of pre-vitamin D into active cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3.
Vitamin D3 is primarily stored in fat cells and the liver and is needed to regulate a wide range of physiological functions.
Vitamin D increases calcium absorption in the small intestines, which promotes bone health, lowers the risk of soft and brittle bones, and may slow down age-related bone loss linked to osteoporosis.
Vitamin D also influences cognitive and neurological functions and is believed to be one of several vitamins for stress and anxiety due to its ability to regulate neurotransmitters such as serotonin and GABA linked to healthy moods and enhanced stress resilience.
Vitamin D deficiency is common, and it’s believed that almost half of all U.S. adults are at risk of low vitamin D levels.
“Symptoms of low vitamin D stores can be non-specific and subtle, making it hard to diagnose vitamin D deficiency early,” explains Dr. Berg.
Here are common signs of vitamin D deficiency:
Fatigue and weakness
Bone pain
Muscle aches
Poor immune function
Depression
Hair loss
Memory problems
Watch the video below to discover the benefits and sources of vitamin K2.
What is vitamin K2?
Vitamin K2 is another fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in blood clotting, regulating calcium metabolism, and maintaining skeletal health.
Blood contains several vitamin K-dependent proteins, also known as matrix Gla protein (MGP), involved in forming blood clots, an important mechanism that regulates wound healing.
Low vitamin K status can impair the activation of MGPs, which affects normal blood clotting processes and increases the risk of bleeding disorders.
Vitamin K also activates proteins in blood vessels that deposit calcium into bone tissue.
Not only does this help increase bone mineral density, a marker of healthy bones, but it also significantly lowers the risk of arterial calcification, a leading risk factor of cardiovascular disease.
Here are common signs of vitamin K deficiency:
Easy bruising
Excessive bleeding
Bleeding gums
Heavy and painful menstruation
Because of its role in blood clotting and calcium balance, maintaining healthy levels of vitamin K2 while pregnant has been found to promote fetal bone growth and reduce the risk of excessive bleeding during childbirth.
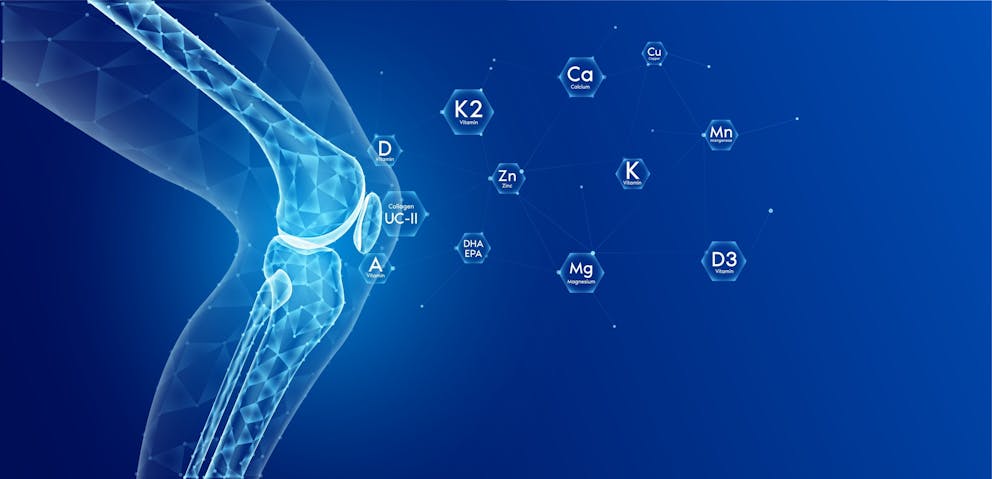
How do vitamin D3 and K2 work together?
Vitamin D3 stimulates the uptake of dietary and supplemental calcium, which raises blood calcium levels.
While calcium is needed for bone growth and skeletal health, elevated calcium levels can lead to calcium deposition in soft tissues such as blood vessels, tendons, and joints.
Soft tissue and vascular calcification is a significant risk factor for coronary heart disease and other chronic diseases, including kidney disease and tendonitis.
Vitamin K2 redirects calcium from soft tissue into the bones, which balances blood calcium levels and helps significantly lower the risk of calcium deposits in arteries and other soft tissues.
Taking vitamin D3 without maintaining an adequate vitamin K2 status can lead to arterial plaque formation and cardiovascular disease, especially in individuals with a high calcium intake.

Three benefits of vitamin D3 and K2
Vitamin D3 and vitamin K2 are two fat-soluble vitamins that work in synergy, and combining these two vitamins can significantly enhance their effectiveness and health benefits.
Here are three benefits of vitamin D3 and K2.
1. Heart health
Combining vitamin D3 and K2 is crucial for heart health and longevity.
A study published in BMJ Open investigated the link between vitamin D3, vitamin K2, and the risk of heart disease and found that “low vitamin K and D status is associated with increased all-cause mortality risk and cardiovascular disease compared with adequate vitamins K and D status.”
2. Bone health
Vitamin D3 and K2 are necessary to ensure adequate calcium deposition into the bone matrix, which enhances the strength and rigidity of the skeletal system.
Taking vitamin D3 and K2 benefits bone mass and skeletal health and lowers the risk of age-related bone issues, including osteoporosis and osteopenia.
3. Skin health
Vitamin D3 and K2 can help improve the skin's health by stimulating collagen production and enhancing skin elasticity.

What’s the best vitamin D3 and K2 dosage?
The best vitamin D3 and K2 dosage depends on several factors, including your health status, age, and your vitamin D and K body stores.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), adults require 600 IU of vitamin D3 daily. However, significantly larger doses of up to 10,000 IU of vitamin D3 daily may be needed to raise insufficient vitamin D levels.
While general vitamin K2 intake recommendations range from 120 mcg daily for men to 90 mcg daily for women, the ideal vitamin K2 dosage depends on how much vitamin D3 you take.
The best ratio of vitamin D3 and K2 is 1000:10, which means you should take 10 mcg of vitamin K2 per 1000 IU of vitamin D3.

Best sources of vitamin D3
Exposing the skin to UVB radiation remains the most natural way to obtain vitamin D3. However, limited sunshine can make getting enough vitamin D to maintain healthy levels difficult.
What’s more, older adults and individuals with a darker skin tone produce less vitamin D, leaving them at increased risk of deficiency.
Vitamin D3 can also be found in small amounts in certain foods, such as fatty fish, cod liver oil, organ meats, and egg yolks.
It’s important to note that food sources typically contribute to less than 20 percent of the daily vitamin D intake recommendations, which explains why vitamin D supplementation has been found to be the most effective and reliable source of vitamin D3.

Best sources of vitamin K2
Vitamin K naturally occurs in two forms: vitamin K1 and K2.
Vitamin K1 is primarily found in plant-based foods, particularly green leafy vegetables and certain vegetable oils.
Vitamin K2 can be obtained from animal products and fermented foods and can also be produced by certain gut bacteria.
It’s thought that vitamin K2 is more effective than vitamin K1 and has a longer half-life in the body, meaning it remains in the bloodstream for extended periods.
Here are some of the best vitamin K2 sources:
Natto (fermented soybeans)
Grass-fed beef
Pasture-raised eggs
Dairy products

Vitamin D3 and K2 supplements
While most vitamin D supplements contain D3, some low-quality dietary supplements are made with D2, a less effective form of vitamin D linked to a higher risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
It’s also important to choose a balanced vitamin D3 and K2 supplement that offers a D3 to K2 ratio of around 1000:10.
Although both vitamin D and K are generally well tolerated, it’s important to note the potential risks of taking excessive doses of D3 and K2.
The National Kidney Foundation warns that too much vitamin K2 may pose risks for individuals with kidney failure.
Vitamin K influences blood clotting and shouldn’t be taken with blood thinning medications such as warfarin or by individuals with bleeding disorders.
In addition, excessive vitamin D intake can lead to vitamin D toxicity, a rare but serious condition that can have serious health consequences, including dangerously elevated calcium levels.
To minimize the risk of side effects and potential drug interactions, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider before adding vitamin D3 and K2 supplementation to your routine.

Key takeaways
Taking vitamin D3 and K2 benefits bone health, lowers the risk of arterial calcification and heart disease, and may benefit reproductive functions.
To maximize the health benefits of vitamin D and K, it’s best to choose a vitamin D3 supplement that contains vitamin K2 in a ratio of at least 1000:10, meaning it delivers 10 mcg of vitamin K2 for each 1000 IU of vitamin D3.
Additional vitamin K2 resources
FAQ
1. What is vitamin K2?
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin that regulates blood clotting and is needed to stimulate calcium deposition into bone tissue.
2. Why should I take vitamin D3 and vitamin K2 together?
Vitamin D enhances intestinal calcium absorption, and vitamin K2 redirects blood calcium into bones, which plays a crucial role in calcium balance and lowers the risk of soft tissue calcification linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
3. How much vitamin D3 and K2 do I need each day?
Most healthcare providers recommend a daily vitamin K intake of 120 mcg for men to 90 mcg for women.
Vitamin D3 requirements can range between 5,000 and 10,000 IU daily depending on vitamin D status, average sun exposure, and skin tone.
4. What are the top vitamin D3 + K2 benefits?
Combining vitamin D3 and K2 benefits skeletal and brain health, can lower the risk of soft tissue calcification and heart disease, and has been found to benefit men with erectile dysfunction.
5. Should I take vitamin D3 and K2 daily?
It’s generally recommended to take vitamin D3 and K2 daily to support optimal calcium metabolism and bone health.
6. Who should not take vitamin D3 and K2?
Individuals with poor kidney function and bleeding disorders should avoid taking extra vitamin D3 and K2.
Vitamin D3 and K2 may interact with anti-seizure drugs, diuretics, and blood thinners, and it’s best to discuss the use of vitamin D3 and K2 with a healthcare provider if you are taking prescription medications.
7. Should I take vitamin D3 and K2 in the morning or at night?
Most people take vitamin D3 and K2 in the morning or at lunchtime with a fat-containing meal to enhance the absorption of these two fat-soluble vitamins.
However, vitamin D can promote healthy sleep, and people with sleep issues may benefit from taking vitamin D3 and K2 before bedtime.
8. How can I get vitamin K2 naturally?
Vitamin K2 is naturally found in fermented foods such as natto and sauerkraut and animal products, including grass-fed beef, pasture-raised chicken eggs, and dairy products.
9. Are vitamin D3 and K2 supplements safe?
Yes, vitamin D3 and K2 supplements are generally considered safe and well-tolerated when taken in appropriate doses.
10. What are the symptoms of vitamin D and vitamin K deficiency?
Common symptoms of vitamin D deficiency include muscle weakness, bone pain, acne, unexplained hair loss, depression, poor cognition, and fatigue.
Vitamin K deficiency can increase the risk of easy bruising, bleeding gums, heavy periods, and excessive bleeding.
11. Can you get vitamin D3 and vitamin K2 from food?
Dietary sources of vitamin D3 include egg yolks, organ meats, fatty fish, and cod liver oils. However, these foods contain only small amounts and won’t be enough to maintain a healthy vitamin D status through diet alone.
Vitamin K2 can be found in grass-fed beef, chicken eggs, dairy products, and fermented foods such as sauerkraut and natto, a Japanese soybean dish.
12. Does vitamin K2 interact with any medications?
Vitamin K2 can interact with blood thinning medications such as warfarin and certain anti-platelet drugs.
13. What is the best ratio of vitamin D3 to K2?
The best ratio of vitamin D3 to K2 is 1000:10, which means a balanced vitamin D3 and K2 supplement should contain at least 10 mcg of vitamin K2 per 1000 IU of vitamin D3.
Previous blog
Can You Drink Wine on Keto? Alcohol and Ketosis
Popular
08/21/2024
43.6K views
05/22/2024
39.1K views
11/18/2024
227.9K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




